Java List 转 树
SQL&Java List 转 树
一般来说,像地区、单位这种数据,一般都是树状结构,但是从数据库查询出来的时候是list,所以就需要把list数据转换成tree数据。
查询的SQL
对oracle数据库来说查询树结构很简单,只需要使用start with就可以:
select *
from 表名 start with 起始条件(比如某个市的code)
connect by prior ID = PID
order siblings by IDmysql则更复杂一点,需要写存储过程并且速度会慢一些,这里不再演示。
不过给两种比较折中的方法:
- 给树型表添加一个code字段,子节点code以父节点code开头,再加上序号;
比如一个节点code是1,那么这个节点的子节点code就是101、102……,在查询的时候就可以使用code like '1%'来查出这个节点及其子节点
(code也可以是固定长度,比如10000,子节点10100、10200……,孙子节点10101、10102……) - 如果表数据不多,可以全部查出来直接在java中构建成树
后续更新:
在mysql中存储树一般有这么几种: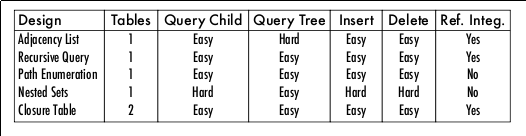
参考:怎样在 MySQL 表中存储树形结构数据? - 卢钧轶的回答 - 知乎
https://www.zhihu.com/question/20417447/answer/15078011
实际操作可以参考https://blog.csdn.net/biplusplus/article/details/7433625
Java构建树结构
这里分享一种在Java中把list转换成树结构的方式
下面放代码:
表结构sql
drop table if exists list_tree;
create table list_tree(
id int primary key comment 'ID',
pid int comment '父ID',
name varchar(20) comment '名称'
);数据就不放了,随便造个几千条就行了
dto结构
import java.util.List;
public class ListTree {
/**
* ID
*/
private Integer id;
/**
* 父ID
*/
private Integer pid;
/**
* 名称
*/
private String name;
List<ListTree> children;
// 省略getter、setter
}然后是具体的转换:
公司代码中使用的是这样的
/**
* 项目中使用的方式
* @return
*/
private static List<ListTree> listToTree1(List<ListTree> listTrees) {
ListTree root = listTrees.get(0);
root.setChildren(findChildren(listTrees, root.getId()));
List<ListTree> result = new ArrayList<>(1);
result.add(root);
return result;
}
private static List<ListTree> findChildren(List<ListTree> srcList, Integer startId) {
List<ListTree> children = new ArrayList<>();
for (ListTree dto : srcList) {
if (Objects.equals(dto.getPid(), startId)) {
dto.setChildren(findChildren(srcList, dto.getId()));
children.add(dto);
}
}
return children;
}我稍微修改了一下,性能更好了:
/**
* 修改后的方式
*/
private static List<ListTree> listToTree2(List<ListTree> srcList) {
List<ListTree> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
Map<Integer, List<ListTree>> pidMap = srcList.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(ListTree::getPid, Collectors.toList()));
resultList.add(srcList.get(0));
setChildren(srcList.get(0), pidMap);
return resultList;
}
private static void setChildren(ListTree dto, Map<Integer, List<ListTree>> pidMap) {
List<ListTree> childrenList = pidMap.get(dto.getId());
if (childrenList == null || childrenList.isEmpty()) {
dto.setChildren(Collections.EMPTY_LIST);
return;
}
dto.setChildren(childrenList);
for (ListTree child : childrenList) {
setChildren(child, pidMap);
}
}五千多条数据,结构4层,修改前耗时300+毫秒,修改后12毫秒,性能提升还是很明显的。
