Web基础之Spring IoC
Spring之IoC
概念
IoC:Inversion of Control,中文通常翻译为“控制反转”,它还有一个别名叫做依赖注入(Dependency Injection)。但实际上依赖注入控制反转的一种表达方式(还有一种叫依赖查找)。什么是控制反转呢,简单来说就是本来上层建筑依赖下层建筑,下载通过依赖注入是下层建筑依附于上层建筑。具体表现就是通过注入的方式,为高级类(接口)添加依赖,注入方式可以为构造方法、set方法和接口注入(用得少,侵入性高)。
而Spring就一种是典型的IoC容器(用来管理bean),并且可以帮助我们管理注入,省去许多麻烦(感觉有点像JVM帮我们管理内存一样)
推荐看一下《Spring揭秘》这本书,讲的非常不错。
快速入门
首先导入IoC相关依赖: spring-context
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>然后是service和dao层的接口及其实现类: 接口及其实现类
public interface UserDao {
public void save();
}
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("保存用户信息");
}
}
public interface UserService {
public void register();
}
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void register() {
System.out.println("注册");
}
} 再然后是xml配置: applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/">
<!--
定义bean
id:唯一标识符
class:bean所对应的类
-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.bilibili.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.bilibili.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>通过spring工厂获取定义的JavaBean:
//加载配置文件,获取spring工厂,从容器中获取dao和service的实现类
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//从容器中获取service
UserService accountService = (UserService) ac.getBean("userService");
System.out.println(accountService);
//从容器中获取dao
UserDao userDao = (UserDao) ac.getBean("userDao");
System.out.println(userDao);放一张被转烂了的图:
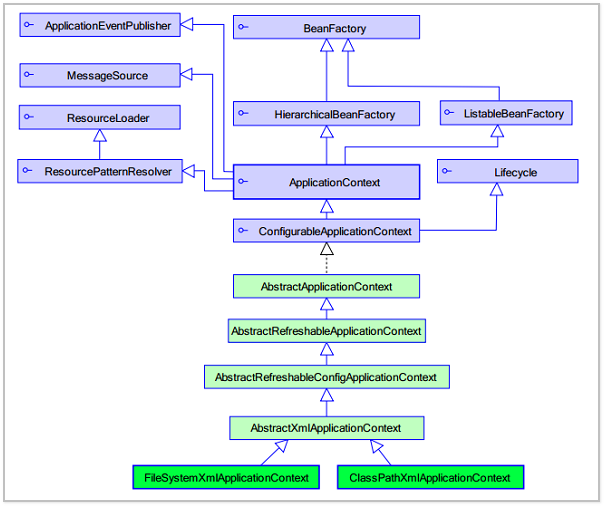
可以看到BeanFactory是工厂的顶层接口,也就是帮助我们管理bean的,ApplicationContext是其子接口。当然,ApplicationContext除了具有BeanFactory的所有功能之外,还有国际化支持。统一资源加载策略、容器内时间发布的特性。同时,两者对于bean的创建时机也不一样,BeanFactory在需要的时候(调用getbean方法)时创建,ApplicationContext会在读取配置之后立即创建。
上面给出了ApplicationContext的使用方法,BeanFactory则不太一样(XmlBeanFactory在3.1之后已过时):
Resource resource=new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml");
BeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
BeanDefinitionReader bdr = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader((BeanDefinitionRegistry) factory);
bdr.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);ApplicationContext 接口的实现类非的三种实现类:
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:它是从类的根路径下加载配置文件,一般使用这种(类根路径为编译后class)
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:它是从磁盘路径上加载配置文件,配置文件可以在磁盘的任意位置。
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext: 注解实现类。
bean标签
bean标签的属性:
id:给对象在容器中提供的唯一标识,用于获取对象class:指定类的全限定类名。用于反射创建对象。默认情况下调用无参构造函数。scope:指定对象的作用范围。<br/>值:singleton:默认值,单例prototype:多例
request:WEB 项目中,Spring 创建一个 Bean 的对象,将对象存入到 request 域中.session:WEB 项目中,Spring 创建一个 Bean 的对象,将对象存入到 session 域中.global session:WEB 项目中,应用在 Portlet 环境.如果没有 Portlet 环境那么 globalSession 相当于 session.init-method:指定类中的初始化方法名称(生命周期相关)。destroy-method:指定类中销毁方法名称(生命周期相关)。
bean的生命周期:
- init-method: 配置bean创建时的初始化方法。
- destory-method:配置bean销毁时的销毁方法。
在ApplicationContext中:
| 周期 | 单例singleton | 多例prototype |
|---|---|---|
| 对象出生 | 当应用加载,创建容器时,对象就被创建了。 | 当使用对象时,创建新的对象实例(getBean被调用) |
| 对象存在 | 只要容器在,对象一直活着 | 只要对象在使用中,就一直活着 |
| 对象死亡 | 当应用卸载,销毁容器时,对象就被销毁了 | 当对象长时间不用时,被java的垃圾回收器回收了 |
创建bean的三种方式:
<!-- 默认无参构造,一般用这种 -->
<bean id="userService" class="com.bilibili.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean>工厂方式:
//静态工厂
public class BeansFacotory1 {
public static Object getBeans(){
return new UserServiceImpl();
}
}
//示例工厂
public class BeansFacotory2 {
public Object getBeans(){
return new UserServiceImpl();
}
}配置方式:
<!-- 静态工厂方法创建对象
class:工厂类的全限定名
factory-method:工厂的静态方法
-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.bilibili.utils.BeansFacotory1" factory-method="getBeans"></bean>
<!-- 实例工厂方法创建对象-->
<!-- 首先配置工厂类的实例 -->
<bean id="beansFactory2" class="com.bilibili.utils.BeansFacotory2"></bean>
<!-- factory-bean:配置工厂类实例对象
factory-method:工厂类中用于创建对象的方法
-->
<bean id="userService" factory-bean="beansFactory2" factory-method="getBeans"></bean>小声BB:工厂都有了还要你spring干啥
依赖注入
面试官:为什么使用spring?
应聘者:因为方便?
面试官:什么?
让spring来管理bean的确方便😂
构造方法注入
构造方法注入需要存在有参构造:
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private String userName;
private int age;
private UserDao userDao;
public UserServiceImpl(String userName, int age, UserDao userDao) {
this.userName = userName;
this.age = age;
this.userDao = userDao;
}
}在xml中使用constructor-arg标签进行注入:
<bean id="userService" class="com.bilibili.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
<!--
如下3个属性是用来指定给象中的哪个具体属性赋值
index: 通过下标来指定构造方法中的属性
name: 通过参数名来指定构造方法中的属性
type: 通过参数的类型(全限定名)来指定构造方法中的属性
如下2个属性是用来指定给对象中的属性赋什么值
value: 赋值基本类型的值 例如:string,int,double...
ref : 被spring管理的其他bean类型。必须是xml中配置的bean
-->
<constructor-arg name="userName" value="王者荣耀"/>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="18" />
<constructor-arg name="userDao" ref="userDao" />
</bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.bilibili.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean>set方法注入
一般使用这种,比构造方法更灵活。
<bean id="userService" class="com.bilibili.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
<!--
property:set方法注入属性
name:set方法的名字后面的内容,小写开头
例如:setUserName - userName
底层: userName - UserName - setUserName
value:基本属性类型的值 例如 String int...
ref:被spring管理的bean类型的值
-->
<property name="userName" value="呜啦啦"/>
<property name="age" value="20"/>
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
</bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.bilibili.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean>命名空间方式注入
其实也是set注入,只不过可以少些一些标签,没什么用。(因为可读性不强)
<!-- 需要在beans标签中添加命名空间:xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" -->
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userDao" class="com.bilibili.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.bilibili.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"
p:userName="呜啦啦" p:age="18" p:userDao-ref="userDao"></bean>
</beans>注入集合属性
先来UserServiceImpl实现类: UserServiceImpl
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private String[] myArray;
private List<String> myList;
private Map<String,String> myMap;
private Set<String> mySet;
public String[] getMyArray() {
return myArray;
}
public void setMyArray(String[] myArray) {
this.myArray = myArray;
}
public List<String> getMyList() {
return myList;
}
public void setMyList(List<String> myList) {
this.myList = myList;
}
public Map<String, String> getMyMap() {
return myMap;
}
public void setMyMap(Map<String, String> myMap) {
this.myMap = myMap;
}
public Set<String> getMySet() {
return mySet;
}
public void setMySet(Set<String> mySet) {
this.mySet = mySet;
}
}然后是xml使用特定标签中注入:
<!--
注入集合属性:
使用set方法注入集合属性:
array:一般用来设置数组
list:一般用来设置list集合
map:一般用来设置map集合
-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.bilibili.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
<property name="myArray">
<array>
<value>a</value>
<value>b</value>
<value>c</value>
</array>
</property>
<property name="myList">
<list>
<value>aa</value>
<value>bb</value>
<value>cc</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="myMap">
<map>
<entry key="key1" value="value1"></entry>
<entry key="key2" value="value2"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="mySet">
<set>
<value>aaa</value>
<value>bbb</value>
<value>ccc</value>
</set>
</property>
</bean>bean除了使用xml进行注入,还可以使用注解进行注入,只不过像JdbcTemplate这种依赖中的类(暂时)就只能使用xml文件来配置注入(context标签需要给beans根标签添加命名空间): 使用xml注入JdbcTemplate
<!-- 加载外部jdbc.properties配置文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!-- 构造器方式注入数据源 -->
<constructor-arg name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- 静态方法配置dataSource -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" >
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</bean>jdbc.properties文件
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root基于注解的IoC
使用注解方式进行注入时需要给beans标签添加命名空间:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- ↑需要添加context命名空间 -->
<!-- 配置注解方式扫描的包:在指定的包下进行扫描,如果发现类上面有注解,让其装配到容器中 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.bilibili"/>
</beans>声明bean的注解:
@Component("beanName"):相当于xml配置的<bean><bean/>标签,注解的value属性值相当于bean标签的id属性,如果不指定value属性,默认bean的id就是类名,首字母小写(Component:组件)<br/>下面三个注解和Component作用一样,只不过更加语义化@Controller:一般用于表现层@Service: 一般用于业务层@Respository: 一般用于持久层
注入相关注解:
@Autowired:自动装配,标注在需要注入的属性上。当使用该注解注入属性时,set方法可以省略,当有多个相同类型的时候,bean的id必须要和属性的名字一致,才能注入成功,否则报错@Qualifier:需要结合@Autowired注解一起使用,在自动注入的基础上,可以给属性注入指定id的bean@Resource:直接注入指定id的bean@Value注解用来给基本类型的属性注入值。可以使用${key}从外部properties配置文件中引入值,需要注意properties配置文件需要在applicationContext.xml中引入
作用范围注解:
@Scope:注解和<bean>标签的scope属性的作用一致。值可以为prototype和singleton(默认)
生命周期注解:
@PostConstruct:声明这个方法是初始化方法,对象被创建的时候调用一次。@PreDestroy:声明这个方式是销毁方法,对象被销毁的时候调用一次。
xml方式和注解方式对比:
| \ | xml | 注解 |
|---|---|---|
| bean定义 | <bean id="" class="" .../> | @Component<br/>衍生:<br/>@Controller<br/>@Service<br/>@Respository |
| bean名称 | 通过id或name属性指定 | 通过上面三个注解的value属性指定 |
| bean注入 | property或p命名空间 | @Autowired按类型注入<br/>@Qualifier配合@Autowired指定<br/>@Resource的name属性,按名称注入 |
| bean作用范围<br/>生命周期 | init-method<br/>destroy-method<br/>scope | @PostConstruct<br/>@PreDestroy<br/>@Scope |
纯注解配置
上面说到像JdbcTemplate这种依赖中的类(暂时)就只能使用xml文件来配置注入,当然也可以使用纯注解进行配置。
主配置:
//声明当前类是一个spring的配置类,用来替代xml配置文件
//获取容器时需要使用AnnotationApplicationContext(@Configuration标注的类.class)
@Configuration
//用于配置容器初始化时需要扫描的包
//和xml配置中<context:component-scan base-package="com.bilibili"/>作用一致
@ComponentScan("com.bilibili")
//导入其他配置类
@Import(JdbcConfig.class)
public class SpringConfig {
//标注这个方法的返回值作为一个bean并且交给spring容器管理,value属性就是bean的id
@Bean("jdbcTemplate")
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(@Qualifier("dataSource") DataSource dataSource){
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
}外部配置:
//引入外部文件,和<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>作用一样
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
public class JdbcConfig {
//使用value注解引用外部变量,这样就不用写死配置了。
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.driverClass}")
private String driverClass;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
//标注这个方法的返回值作为一个bean并且交给spring容器管理,value属性就是bean的id
@Bean("dataSource")
public DataSource getDataSource(){
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClass);
dataSource.setUrl(url);
dataSource.setUsername(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
return dataSource;
}
}测试类:
public class SpringConfigTest {
@Test
public void getJdbcTemplate() {
//使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext实现类来获取工厂
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = (JdbcTemplate)ac.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
System.out.println("jdbcTemplate = " + jdbcTemplate);
}
}在Junit测试类中注入
在每个单元测试类中,我们都需要获取Spring容器,然后获取要测试的类:
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
accountService = (AccountService) ac.getBean("accountServiceImpl");
}那么能不能直接在测试类中注入要测试的bean呢?
当然是可以。
首先添加依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- spring5及以上版本要求junit的版本必须是4.12及以上。 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.0.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>然后给测试类配置注解:
//配置spring的单元测试运行器,自动创建spring容器
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//配置容器创建时依赖的配置
//xml文件方式,直接给value赋值(注意前缀classpath:)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
//纯注解方式,给classes属性赋值
@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class)
public class AccountServiceImplTest {
//依赖注入
@Resource(name = "accountService")
private AccountService accountService;
}然后就可以愉快地在测试类中使用注入的依赖了。依赖少的时候好像并没有方便多少😅
